 |
According to foreign media reports, NASA scientists and engineers plan to develop nuclear-powered rockets so that future astronauts can stage far-reaching space travel and explore the depths of Mars and the solar system. Compared to traditional rockets that use chemical fuels, the use of nuclear fusion rockets can shorten the exploration time of the solar system. Engineers are drafting plans to use nuclear rockets in a Mars exploration mission to be implemented in 2033.
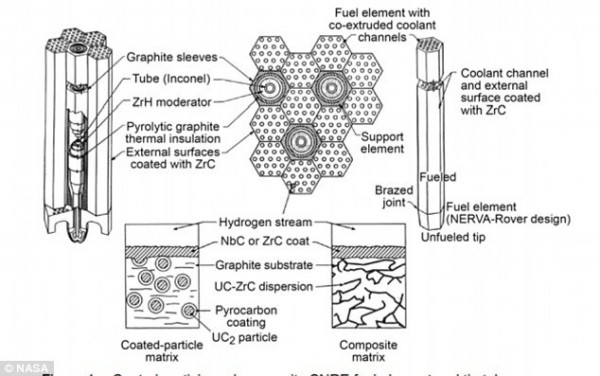
With the same propulsion, nuclear rockets weigh only half as much as chemical rockets. By design, nuclear reactors using uranium-235 will be used to heat liquid hydrogen in a reactor, turning it into ionized hydrogen gas or ions, and then passing through rocket nozzles to generate propulsion.
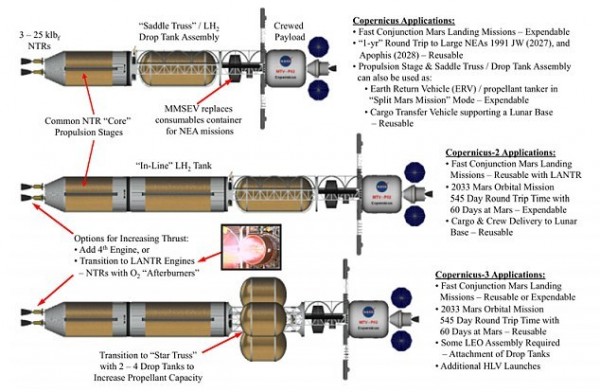
In an official NASA space document, engineers outlined how a nuclear power propulsion system can drive spacecraft forward in space. The proposed nuclear-powered spacecraft - known as "Copernicus" - will consist of separate cargo holds and crew compartments, each driven by a nuclear thermal propulsion class. The propulsion unit consists of three engines, each generating approximately 25,000 pounds (about 11,000 kilograms) of thrust.

It is estimated that the Copernicus spacecraft can fly 40 million miles (about 64.40 million kilometers) within 100 days and reach Mars. In contrast, the "Mars Science Laboratory" equipped with the "Magic" was used for 253 days to reach this red planet.
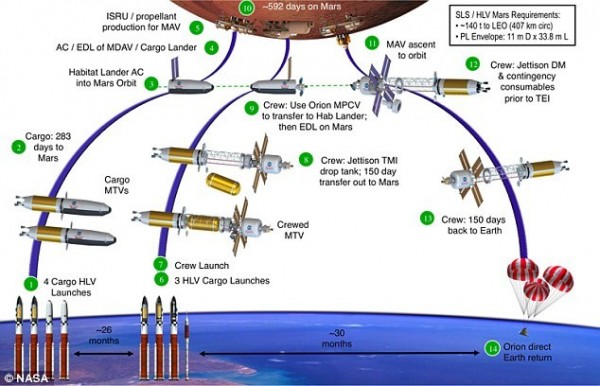
In 1968, Nevada, USA, the "Sun God 2a" nuclear rocket engine was tested for a total of 32 minutes. "Sun God 2a" is the most powerful nuclear rocket that has been tested so far. According to the plan, a Mars exploration mission in 2033 will launch two cargo bays, deploy equipment on the surface and orbit of Mars, and then dispatch astronauts.
The current design of the Copernicus spacecraft can reach Mars in about 130 days. If the spacecraft is improved to carry more propellant, it can be reduced to 100 days. If the equipment and cargo were first sent to Mars via seven launches on the ground and the astronauts were to be launched again, the possibility of controlling the Mars travel time for 90 days also existed.
Hesco Barrier,Hesco Flood Barrier,Hesco Barrier Mill,Military Sand Wall Hesco Barrier
Anping County Kairong Wire Mesh Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.krmeshfence.com