Table of Contents
- Overview
- What is Dissolved Oxygen?
- Definition of Dissolved Oxygen
- Importance of Dissolved Oxygen
- Types of Dissolved Oxygen Sensors
- Applications of Dissolved Oxygen
- How to Measure Dissolved Oxygen
- Benefits of Monitoring Dissolved Oxygen
- Factors Affecting Dissolved Oxygen Levels
- Water Solubility of Oxygen
- Maintenance and Calibration of Dissolved Oxygen Sensors
Overview
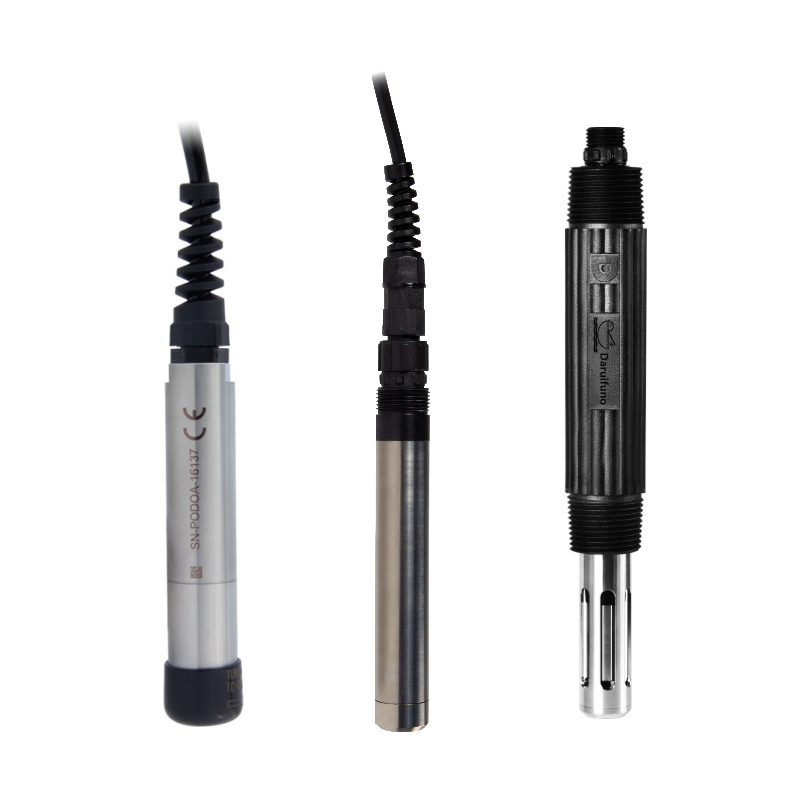
Explore dissolved oxygen sensors and probes for water, wastewater, industrial, aquaculture, and more, and understand the importance of its measurements. Dissolved oxygen sensors, also called dissolved oxygen probes, are important instruments for monitoring the health of aquatic environments. By accurately measuring the amount of oxygen in the water, these sensors help ensure optimal living conditions for aquatic life and support various water quality management strategies.

Â
What is Dissolved Oxygen?
Dissolved oxygen (DO) refers to the oxygen that is present in water, which is crucial for the survival of aquatic organisms. The oxygen is dissolved in water and is available for aquatic life such as fish, crustaceans, and microorganisms to breathe. This process is an essential aspect of maintaining aquatic ecosystems.

Definition of Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is the oxygen dissolved in water that is available for respiration by aquatic organisms. It is measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L) and is a key indicator of water quality. A high concentration of dissolved oxygen signifies a healthy aquatic environment, while low levels can lead to hypoxia, which can harm aquatic life.
Importance of Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is vital for the health of aquatic ecosystems. It supports the respiratory processes of aquatic animals, helps in the breakdown of organic matter, and is an indicator of water quality. Insufficient levels of dissolved oxygen can cause problems like fish kills, which directly affect the ecosystem and water quality management strategies.
Â
Types of Dissolved Oxygen Sensors
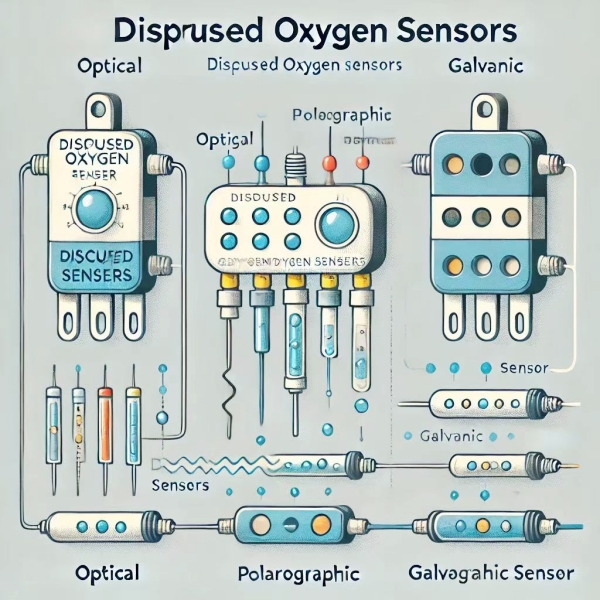
There are several types of dissolved oxygen sensors, each with its specific features and application areas:
Optical Dissolved Oxygen Sensors: These sensors use fluorescence technology for accurate and stable measurements. They offer rapid response times and require less maintenance than traditional sensors.
Polarographic Sensors: These sensors use electrochemical reactions to measure oxygen levels. They are widely used for general-purpose water quality monitoring.
Galvanic Sensors: Similar to polarographic sensors, galvanic sensors also use electrochemical principles but are suitable for specific applications with less maintenance.
Applications of Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen sensors are used in a wide range of applications:
Aquaculture: Monitoring DO levels ensures optimal conditions for fish and other aquatic organisms.
Water Treatment: Ensuring proper oxygen levels in wastewater treatment plants helps the biological treatment process.
Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring rivers, lakes, and oceans helps track ecosystem health and detect pollution.
Industrial Processes: Certain industries, like brewing and pharmaceuticals, require accurate oxygen levels for optimal production.
Â
How to Measure Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is typically measured using specialized sensors, such as optical, polarographic, and galvanic sensors. The measurement can be performed manually or continuously in real-time with automated systems. The sensors are calibrated using known oxygen concentrations to ensure accurate readings.
Â
Benefits of Monitoring Dissolved Oxygen
Regular monitoring of dissolved oxygen provides numerous benefits:
Improved Aquatic Life: Ensures that water environments are healthy and supports the survival of aquatic species.
Enhanced Water Quality: Maintaining optimal oxygen levels promotes clean, clear, and healthy water for various uses.
Early Detection of Environmental Stress: Identifies sudden drops in DO that may indicate pollution or eutrophication, allowing for quick intervention.
Â
Factors Affecting Dissolved Oxygen Levels
Several factors influence dissolved oxygen levels, including:
Temperature: Higher temperatures generally decrease the solubility of oxygen in water.
Altitude: Higher altitudes result in lower atmospheric pressure, reducing the amount of oxygen that can dissolve in water.
Pollution: Organic matter decomposition consumes oxygen, reducing DO levels in polluted waters.
Salinity: Higher salinity decreases the solubility of oxygen in water.
Â
Water Solubility of Oxygen
Water's ability to dissolve oxygen is limited by temperature, pressure, and salinity. Cold water can hold more oxygen than warm water, and freshwater typically holds more dissolved oxygen than seawater. Understanding this relationship is important for managing aquatic environments effectively.
Â
Maintenance and Calibration of Dissolved Oxygen Sensors
Maintaining and calibrating dissolved oxygen sensors is essential for ensuring accurate readings. Regular calibration with standard solutions and routine checks for wear and tear will help extend the sensor's lifespan. Optical sensors, in particular, require less maintenance compared to electrochemical sensors, as they do not require electrolyte replacement.
Â
For more than a decade, Daruifuno has been focusing on the R&D and production of water quality analysis instruments. Our extensive product line includes not only dissolved oxygen sensors and dissolved oxygen probes, but also analyzers/meters, controllers and sensors/probes/electrodes for key water quality parameters such as pH, ORP, conductivity, turbidity, COD, dissolved oxygen, ammonium and chlorine. If you are interested in any of our products, please feel free to contact us.
Dissolved Oxygen Sensor,Dissolved Oxygen Probe,DO Sensor,DO Probe
Suzhou Delfino Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.daruifuno.com