According to the survey by the Department of Environment and Resources Comprehensive Utilization of the National Development and Reform Commission, China's energy utilization rate is about 33%, which is 10% lower than that of developed countries. The energy consumption of the younger generation is more than twice the world average. The State Council's decision on strengthening energy conservation work pointed out that energy issues have become an important factor restricting China's economic and social development. From a strategic and global perspective, we must fully understand the importance of doing a good job in energy work, and attach great importance to energy security to achieve sustainable energy development. .
The fundamental way out for solving the problem of energy in China is to adhere to the principle of development and conservation, save priority, and vigorously promote energy conservation and consumption reduction to improve energy efficiency. The 11th Five-Year Plan for the Implementation of the Ten Key Energy-Saving Projects issued by the Development and Reform Commission and other eight departments clearly defined the main task of building energy conservation as one of the top ten energy-saving projects.
China's building energy consumption accounts for about 27% of the country's total energy consumption. This building is one of the important contents of China's energy-saving work. The No. 143 issued by the Ministry of Construction of the People's Republic of China provides for the regulation of energy conservation in residential buildings and public buildings. On September 15, 2006, the Ministry of Construction issued a implementation opinion that put forward the implementation of building energy conservation goals to achieve the goal of saving 1.1 billion tons of standard coal at the end of the 11th Five-Year Plan. Among them, through strict supervision and strict implementation of energy-saving design standards, the municipality is promoted. And implement high-level energy-saving standards in severe cold and cold regions. Newly built residential buildings in cold and cold regions will achieve energy saving of 21 million tons of standard coal, and new residential buildings in hot summer and cold winter areas will achieve energy-saving 24 million tons of standard coal in hot summer and warm winter areas. Energy saving 2.2 million tons of standard coal, new public buildings across the country to achieve energy saving 22.8 million tons of standard coal, a total of 70 million tons of standard coal energy saving through the existing building energy-saving renovation, deepening the heating system reform to strengthen the government office buildings and large public buildings energy-saving operation management And the transformation and realization of energy-saving 30 million tons of standard coal, the area of ​​energy-saving renovation of existing buildings in large cities should account for 25% of the total area of ​​existing buildings, medium-sized cities should be reduced to 15%, and small cities should be reduced to 10%; Application of energy-saving lighting fixtures to achieve energy saving 10.4 million tons of standard coal, solar energy, shallow ground energy and other renewable energy applications occupy new buildings The proportion of the product is more than 25%. The Ministry of Construction organizes the China Academy of Building Research and other units in the current G261995 civil building energy-saving design standards (heating residential building part) G 134-2001 hot winter cold area residential building energy-saving design standards>, G752003 summer The drafting of the national standard residential building energy-saving design standards drafted on the basis of three industry standards such as the energy-saving design standards for residential buildings in the hot and warm winter area has been compiled in August 2006. The current standards-setting group is still in the country. The unit solicited opinions. Not long ago, the Ministry of Construction and the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine jointly issued the GB50411-2007 (Building Quality Acceptance Specification for Jianjian Energy-saving Project, which will be implemented on October 1, 2007. This series of regulations and regulations The implementation of the standard has further improved the national regulations and standards system for building energy conservation, providing a strong technical guarantee for the implementation of building energy-saving design standards and related building energy-saving requirements and operative technical means for building energy-saving projects. The quality acceptance of construction provides a unified technical requirement for the strengthening of building energy management
1 Advantages of external thermal insulation for exterior walls In the past 10 years, China's building energy conservation has seen a variety of external wall insulation technologies using different materials and different practices on the basis of learning and introducing advanced foreign technology. The self-insulation of building maintenance structures is also He has strengthened his efforts and received good insulation and energy saving effects and accumulated a certain amount of experience. Among them, the development of external thermal insulation technology is the fastest. The superiority of external thermal insulation is mainly reflected in the following aspects: external thermal insulation of the external wall can avoid the wall temperature, condensation, water and mildew caused by the cold (heat) bridge through the comprehensive covering of the building maintenance structure. The occurrence of the problem.
Since the structural layer is located on the inner side of the system, the external environment has little effect on it, so that its high thermal storage performance is fully utilized. When the indoor is subjected to unstable heat waves (such as indoor temperature rise or fall), the structural layer can pass heat absorption or The release of the heat balance temperature is beneficial to the stability of the indoor temperature and can greatly improve and improve the waterproof and airtight performance of the wall.
The thermal insulation layer is located on the outer side of the building envelope to avoid or greatly buffer the stress and stress accumulation caused by structural deformation caused by external temperature changes, avoiding structural damage caused by rain and snow freezing and warm drying cycle, greatly reducing external harmful gases and The erosion of the structure by other substances protects the main structure and effectively improves the durability of the main structure.
In the case of energy-saving renovation of existing buildings, the external insulation of the external wall will not have a greater impact on the residents and will not reduce the building area. Although the cost per unit area of ​​the external thermal insulation project is relatively higher than that of the internal insulation, it increases the use area by 1.8% to 2.0% compared with the internal insulation.
The exterior thermal insulation technology is adopted, and the building has good thermal stability, so the house is warm in winter and cool in summer.
2 Main categories of external thermal insulation G144-2004 (The external thermal insulation engineering technical regulations specify five types of external thermal insulation systems, followed by EPS (expanded polystyrene) thin plastering exterior insulation system , EPS powder granule insulation slurry external wall insulation system, EPS board cast-in-place concrete external wall insulation system, EPS steel wire grid plate cast-in-place concrete exterior wall insulation system and mechanical fixed EPS steel wire grid plate exterior insulation system. At present, the most commonly used is the EPS board thin plaster external wall insulation system and the rubber powder EPS granule insulation slurry external wall insulation system. The latter is suitable for use in the case where the thickness of the EPS powder thermal insulation slurry calculated according to the building energy-saving requirements does not exceed 100 mm, and is now more and more widely used in areas such as hot summer cold and hot summer and warm winter.
With the building energy-saving indicators gradually increased to 65% in recent years, the country has also developed polyurethane high-efficiency external insulation technology, composite external insulation technology, extruded polystyrene board external insulation technology, rock wool external insulation technology and foam glass external insulation technology. In order to enrich the technology and process of China's building exterior wall thermal insulation engineering, the guidance on the application of polyurethane rigid foam exterior insulation engineering technology was strengthened. On May 19, 007, the Ministry of Construction issued the "No. Technical guidelines for exterior insulation engineering (hereinafter referred to as the “Guidelinesâ€). The following mainly introduces the technology and application of polyurethane rigid foam exterior insulation system.
The polyurethane rigid foam exterior insulation system is composed of a polyurethane rigid foam insulation layer, an interface layer, a surface layer, a facing layer or a fixing material.
3.2 Polyurethane rigid foam external wall insulation system composition material 3.2.1 Polyurethane rigid foam polyurethane rigid foam characteristics Polyurethane foam can be changed by the composition of raw materials, formulation ratio, synthesis conditions, etc. to obtain different hardness, fire resistance , high temperature resistance, chemical resistance and foam with different mechanical strength. Polyurethane rigid foam is a kind of low-density microporous material with closed cell structure, which has the characteristics of light weight, high specific strength, small thermal conductivity, good thermal insulation performance, low water absorption and convenient construction and operation. The thermal conductivity of polyurethane foams is affected by the temperature of use and is related to the type and density of gases in the foam. Generally, the thermal conductivity is proportional to the change in density. When the density is 35kg/m3, the thermal conductivity of the urethane rigid foam is lower. The ideal density is 3545kg/m3, and the thermal conductivity can be maintained at 0.018 ~ 0.025W/( mK), when the density is small (for example, less than 30kg/m3), the thermal conductivity increases, which is mainly because the proportion of the open-cell structure increases when the density of the foam is too low, resulting in an increase in thermal conductivity. Many physical properties of polyurethane foam depend on its cell structure. For rigid foams, the cell is preferably closed cell structure and the higher the cell closedness, the lower the water absorption of the product. The better the airtightness, the better the thermal insulation performance. Excellent. Polyurethane rigid foam can be produced either in factory or on site, which is an advantage that other foams such as polystyrene and polyethylene do not have.
Polyfoaming Principle of Polyurethane Rigid Foam Polyurethane rigid foam is prepared by reacting a difunctional or polyfunctional isocyanate with a polyfunctional hydroxyl-containing compound under the action of a catalyst or the like.
The cell size is dependent on the foam stabilizer adjustment. The method of synthesizing the polyurethane foam generally includes a prepolymerization method, a semi-prepolymerization method, a one-step method, and the like. The raw materials to be used are polyols, polyisocyanates, catalysts, foaming agents, foam stabilizers and flame retardants, anti-aging agents, anti-mold agents and the like. Polyols mainly include polyether polyols and polyester polyols, which are low molecular weight and high viscosity compounds. Polyols used in polyurethane rigid foams have a molecular weight of less than 1300 and a hydroxyl number of 700 or less. The functionality is 3 and the other is more diverse. Alcohol is castor oil and its derivatives. Castor oil is generally blended with other polyols to improve the softness of polyurethane rigid foam.
The chemical reaction of polyurethane foam systems, such as chain extension, foaming and cross-linking, is related to the structure, functionality, molecular weight, etc. of the materials involved in the reaction.
In the foaming system of the polyurethane foam, the isocyanate is generally used in an amount larger than the active chlorine-containing compound, that is, the isocyanate amount index is more than 1 (the isocyanate index is the ratio of the number of isocyanate equivalents to the equivalent number of the chlorine-containing compound). Usually the isocyanate index is taken to be 1.05 in the foaming system, ie an excess of 5% isocyanate. For this purpose, the end of the chain extension end product during the foaming process should be an isocyanate-containing group. The principle of preparing a rigid polyurethane foam is foaming according to physical action, that is, the use of a low-boiling halogenated product to be vaporized by heat to achieve foaming.
Environmental requirements for polyurethane rigid foams Early polyurethane materials contained a large amount of organic solvents, coal tar and other harmful substances to the environment and human body. In recent years, great progress has been made in the study of solvent-free and low-free TDI of polyurethane materials. In addition, important environmental protection is reflected in ODP (Ozone Depletion Potential), which requires ODP to be zero or close to zero. For a long time, rigid foam polyurethane has been foamed with fluorotrichloromethane (CFC-11, -11). This is because CFC-11 is non-flammable, non-corrosive, low in toxicity, suitable in boiling point, stable in chemical properties, and safe to use. Rigid foam has excellent performance, high mechanical strength, high dimensional stability, low thermal conductivity and good processing. However, in the mid-1970s, scientists discovered that after Freon (F-11) volatilized into the atmosphere, it reacted with ozone to consume stratospheric ozone. To this end, in 1987, the United Nations Environmental Materials Agency (UNEP) developed the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, which entered into force on July 1, 1997. This protocol determines that lowering the ODP value has become the main direction of the development of the polyurethane foam industry and an important form of environmental protection.
The guidelines stipulate that polyurethane rigid foams should be flame retardant and environmentally friendly materials. The foaming agent must use environmentally friendly non-CFC materials such as HCFC, HFC, alkanes, water or a mixture thereof.
1 Polyurethane rigid foam main raw material performance index A component material: should be no CFC, meet environmental protection requirements, transparent appearance, uniform non-layering; B component material t should be polymeric MDI, performance can be as follows: NCO based 2 polyurethane rigid foam Material performance indicators (see Table 1) Table 1 Polyurethane rigid foam material performance index items can be bath time / h tensile bond strength 1 / kPa Table 2 surface glue performance indicators 1 indicators play the original strength water resistance freeze-free Sexual resistance strength / MPa compression ratio of 150, and destroying the halogen on the polyurethane hard foam 100, K destruction interface on the poly M cool foam >100, and the destruction interface on the polyurethane rigid foam 矣 3 Bu 0 Note: 0) Bonded to a polyurethane foam board.
Tester project indicators require spray method to be poured into the method of adhesion or dry hanging method. Apparently different 3538 Fen 40 tensile bond strength / kpa island 150 150 tensile strength / kPa20 (F200200 elongation at break / % race 75 = 5 5 water absorption /% dimensional stability (48h) / 9fcmx raspberry 2.0-30 V average burning time; S70 flame retardant performance average burning range / mm 耷 40 smoke density grade (SDR) 75 3.2.3 broken fiber mesh due to The plaster is generally cement-based and alkaline. Therefore, it is necessary to use an alkali-resistant glass fiber mesh. The alkali-resistant glass fiber mesh is made of alkali-resistant glass fiber with a certain amount of chromium added or coated with a surface. The alkali-resistant polymer is made of ordinary glass fiber. The alkali-resistant glass fiber is embedded in the plaster to improve the mechanical strength of the plaster layer, ensure its continuity, disperse the shrinkage stress and temperature stress of the surface layer, and avoid stress concentration. To prevent plastic cracks and dry shrinkage cracks in the surface layer. If the surface glue is blended with staggered short fibers, the system has better crack resistance, impact resistance and durability.
The alkali-resistant mesh cloth must have good tensile strength and fracture stress in the two-dimensional direction. At the same time, its fracture strain should not be too large. The technical performance requirements are shown in Table 3. Table 3 Alkali-resistant glass fiber mesh performance index i:l project indicators require test method alkali-resistant fracture strength retention rate (warp, weft) /% 50 GH9 alkali-resistant fracture strength (warp, weft) N / 50mm) Note: 1 and the cement material between the tensile bond Knot strength; 2 tensile bond strength between polyurethane rigid foam material and the atrial material of table a: 3 tensile direction is a parallel thousand spray base table (ie, the tensile force surface is perpendicular to the surface of the spray base); The stretching direction is perpendicular to the thickness of the injection cavity (ie, the tensile force surface is parallel to the thickness of the casting cavity) - in order to meet the requirements of low deformation, crack resistance, impact resistance and water resistance, the surface glue is generally mixed A certain amount of fiber cement cement (or fine sand mortar). The plastering paste is usually made of cement or other inorganic cementitious materials, molecular polymers, fillers, fibers and the like. Applying a thin layer of plaster to the outer surface of the polyurethane rigid foam ensures the mechanical strength and durability of the external insulation system. The thin plaster and the insulation layer must have a high bond strength, and have good water resistance, freeze-thaw resistance, weather resistance. In order to meet the impact resistance, it must also have good flexibility, and at the same time, Has good operability. The technical performance requirements are shown in Table 2. 3, 2.4 Adhesive polyurethane rigid foam external wall insulation system. The binder used in the construction may be two-component or one-component type D binder and concrete (or block). ) The base layer and the insulation layer must have sufficient bonding strength, and the construction should also have a certain operational adjustment time. The shrinkage rate of the binder during coagulation hardening and dehydration drying should be as low as possible to avoid excessive internal stress and affect the bonding quality between the matrix and the polyurethane rigid foam. The technical performance requirements of the adhesive are shown in Table 4. Table 4 Adhesive construction Adhesive performance index item Lu index requirements Tester alone operation time / hL.5-4.0 and cement mortar original strength body 600 tensile bond strength ZkPa water resistance 400C149, the hardness of the polyurethane hard original is 150, the R failure interface is on the polyurethane hard foam C/1'3049 foam tensile bond water resistance 100 and the damage interface on the polyurethane rigid foam 丨 freeze-thaw resistance> m, a The damage surface is in the polyurethane hard foam t: Note: 1 The polyurethane rigid foam insulation material actually used in the project is used, that is, if the plate bonding surface has a curved layer T when it is actually used, the surface layer material should not be removed during the test. The system of 3.2.5 veneer veneer bricks must adopt sufficient safety measures if it is made of veneer bricks, and has been tested and verified to meet the relevant national standards.
As a finishing layer for exterior insulation systems, high performance waterborne architectural coatings should be the best choice. G149-2003 stipulates that architectural coatings must have good compatibility with polyurethane rigid foam systems and that product performance should comply with relevant exterior wall architectural coating standards. In addition, the coating used for the exterior insulation system finish should also have the following characteristics: good water repellency and breathability, so that the external wall insulation wall can maintain good breathing function (breathability) and thermal insulation performance. It is stipulated that the 5mm thick protective layer of the external thermal insulation system shall be immersed for 24h, and the water absorption requirement shall not exceed 1000g/m2; the water vapor temperature density of the outer thermal insulation system protective layer and the veneer coating shall not be less than 0.85g/(m2h); At the same time, the impermeability of the plastering layer is required to be impervious to water for 2 hours.
Light-colored coatings have a greater reflection coefficient of solar radiant energy than darker coatings. Solar radiant heat is the main heat source that affects the building's thermal process. Summer temperature is high. Radiant heat. Large coating color affects large winter temperatures. Low radiant heat, and the coating color has little effect. Therefore, the choice of color for exterior insulation coatings should be based on summer insulation. Try not to choose coatings that are too dark.
G144-2004 stipulates that the service life of external thermal insulation projects shall not be less than 25 years. The service life of exterior wall coatings is not only related to the quality of exterior wall coatings, but also related to factors such as base layer, construction quality, environmental conditions of use, paint color and maintenance. Therefore, it is best to use durable exterior wall paints, especially color pastes. It is preferred to choose inorganic pigments with good color retention and timely maintenance and renovation.
33 Polyurethane rigid foam exterior insulation system engineering design The design of polyurethane rigid foam exterior insulation project should be combined with the climate division of the area where the building is located, in accordance with the national energy conservation design standards and the specific energy saving technical requirements of the project. After the technical and economic comparison, the structure and structure of the polyurethane rigid foam external wall thermal insulation system, the thickness index of the thermal insulation layer, etc., and the construction method of the polyurethane rigid foam external thermal insulation system are determined.
The thermal performance of polyurethane rigid foam exterior wall thermal insulation composite wall shall be calculated according to GB50176 civil building thermal design specification or its thermal insulation moisture resistance performance shall comply with the current building energy-saving engineering series such as GB50176G26G134 and G75. The relevant provisions of the design standards; the polyurethane rigid foam exterior insulation system applied to public buildings should also comply with the relevant provisions of GB 50189 Public Building Energy Conservation Standards).
According to the structure type of different buildings, the quality regulations, technical requirements and external surface treatment of polyurethane rigid foam external thermal insulation engineering are proposed. Whether it is masonry structure, light steel structure, frame-filled wall structure, short-limb shear wall-filled wall structure or full shear wall structure, the main structure and external wall of the building should meet the requirements of current national standards and regulations. The structural load of the polyurethane rigid foam exterior insulation system is included in the calculation of the main structural load.
Penetration of external walls, balconies, holes, etc. should be done at the same time as the insulation node treatment; at the same time, the top of the wall insulation should be treated with waterproof nodes.
4 Conclusion G144-2004 external wall thermal insulation engineering technical regulations stipulates EPS (expanded polystyrene) board thin plastering exterior insulation system and other five types of exterior insulation system after years of technical development and engineering practice, Has accumulated a certain amount of experience. Polyurethane rigid foam is a high-performance thermal insulation material urethane hard foam external wall thermal insulation system as a new type of external wall thermal insulation system with good comprehensive performance. It has a good development prospect in the field of building energy conservation in China. The technical guidelines for the urethane rigid foam exterior insulation project recently issued by the Ministry of Construction are of great significance for promoting the promotion and application of polyurethane rigid foam external wall insulation system in China and achieving higher building energy conservation goals. However, the experience of polyurethane rigid foam external wall insulation system in the application of building energy-saving projects in China is not much, including design, construction, supervision and quality inspection, etc. We should timely control and prevent the problems that arise. Strengthen the specialization and large-scale production of polyurethane rigid foam raw materials, strengthen the standardization, standardization and industrialization of products and accessories matched with polyurethane rigid foam materials; strengthen the special template for the construction of polyurethane rigid foam external thermal insulation system with pouring method. Standardization and industrialization Strengthen the localization and industrialization of special production and construction equipment and equipment for the rigid and external thermal insulation system of polyurethane rigid foam, and the standardization and specialization of special test equipment and equipment supporting the performance test of polyurethane rigid foam external thermal insulation system. Turn. The most important measure to ensure the quality of the external thermal insulation project is to produce quality qualified products in accordance with the standards, and strictly carry out design, construction and acceptance according to relevant technical regulations.
(Finish)
Aluminum Stub End has many advantages such as long service life, light weight, good heat resistance, good corrosion resistance, good heat preservation, high impact. According to the grad of the aluminum, it can be divided into Aluminum 1060 Stub End, Aluminum 5083 Stub End, Aluminum 6061 Stub End, Aluminum B241 Stub End.
Item Cold: aluminum stub end
Diameter: 1" 1.5" 2" 2.5" 3" 3.5" 4" 5" 6"
Wall thickness: 1.5mm,1.8mm,2.0mm,2.5mm
Surface treatment: Polish/Raw
Material: Aluminum 6061/ Aluminum 6063 /Aluminum 5083
MOQ: 50 pieces
Packing: Plastic bags and carton boxes
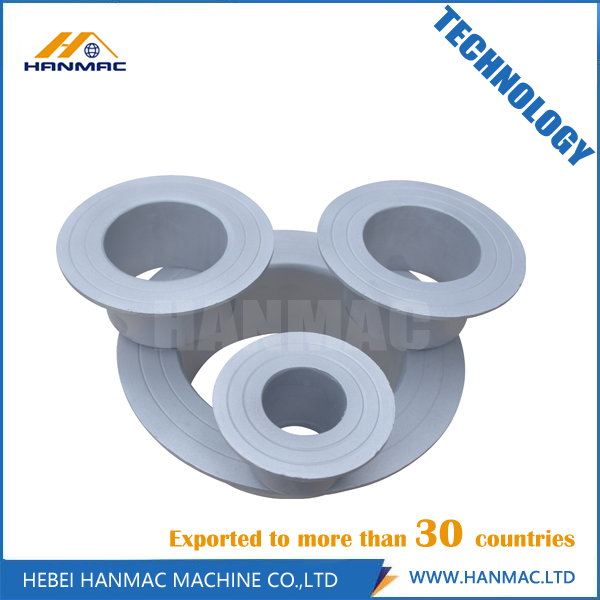

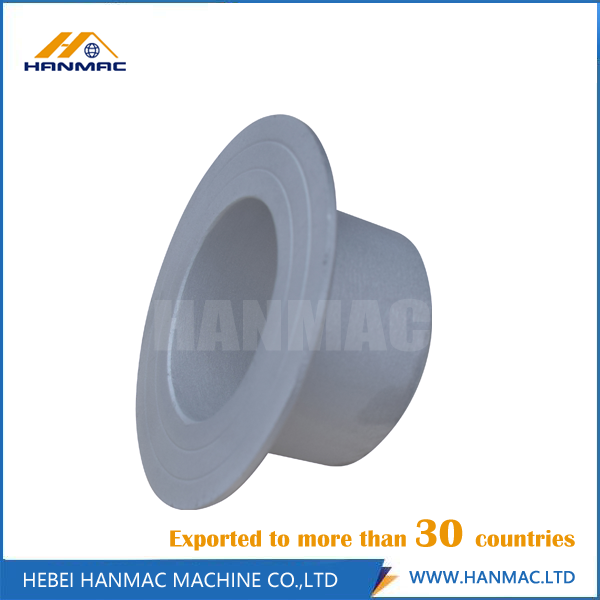
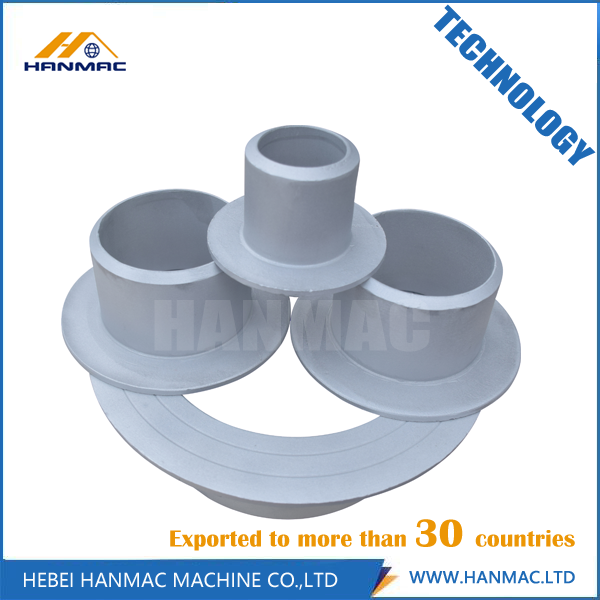
Aluminum Stub End
Aluminum Stub End, Aluminum 1060 Stub End, Aluminum 5083 Stub End, Aluminum 6061 Stub End, Aluminum B241 Stub End
HEBEI HANMAC MACHINE CO., LTD. , https://www.chinahanmac.com